- Sustained efficacy 5 years after injection in REFLECT Phase III trial
- Continued benefit at 5 years in bilaterally treated patients: clinically meaningful improvement of at least 15 letters relative to their observed nadir (worst visual acuity)
- 75% of bilaterally treated patients experienced Clinically Relevant Recovery* of visual acuity versus their nadir
- Favorable safety profile confirmed at 5 years
Paris, France, February 12, 2025, 7:30 am CET – GenSight Biologics (Euronext: SIGHT, ISIN: FR0013183985, PEA-PME eligible), a biopharma company focused on developing and commercializing innovative gene therapies for retinal neurodegenerative diseases and central nervous system disorders, today reported final efficacy and safety results at the conclusion of the REFLECT Phase III clinical trial with LUMEVOQ® (GS010; lenadogene nolparvovec). The results show that five years after a one-time administration of the gene therapy, the visual acuity improvement among patients with LHON (Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy) was sustained while maintaining a favorable safety profile. Bilateral injections provided an additional effect compared to unilateral treatment, demonstrated in some of the responder rate analyses.
“The latest REFLECT data confirms that the improvement seen with lenadogene nolparvovec is sustained 5 years after treatment has been given, including the additional benefit observed in participants receiving a bilateral intravitreal injection of the gene therapy,” said Prof. Patrick Yu-Wai-Man, MD, PhD, Professor of Ophthalmology and Honorary Consultant Neuro-ophthalmologist at the University of Cambridge, Moorfields Eye Hospital, and the UCL Institute of Ophthalmology, United Kingdom, and International Principal Investigator of REFLECT. “Importantly, REFLECT participants receiving a bilateral injection had a comparable safety profile to those treated unilaterally.”
The findings reinforce the results observed at 4 years post-treatment administration, which were reported in March 2024.
Sustained and meaningful efficacy at Year 5
The evolution of the visual acuity over time shows that visual improvement after lenadogene nolparvovec treatment was maintained over 5 years in all subjects. The improvement of placebo eyes highlights the consistent contralateral treatment effect observed in all clinical trials (which was also documented in sham-treated eyes in the REVERSE1 and RESCUE2 trials). (See Graph 1.)
Graph 1: Evolution of Best-Corrected Visual Acuity (BCVA) Over 5 Years of Follow-Up
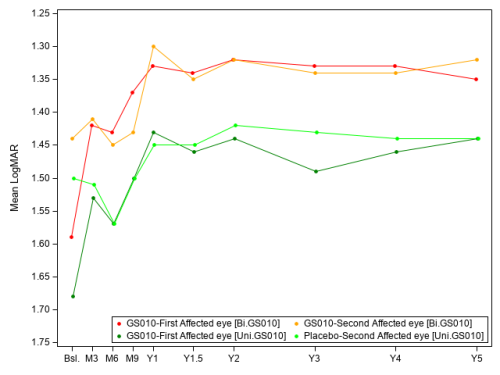
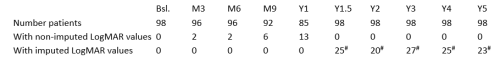
#LOCF (Last Observation Carried Forward) imputation aligned with the study’s statistical analysis plan. Imputed/non-imputed data used for both eyes as applicable. Database lock: December 31, 2024.
Because of the severity of the acute phase in LHON, vision could still deteriorate to a low point or nadir in the initial period of the trial. This characteristic of the disease makes the observed nadir (i.e., the worst BCVA recorded from baseline to Year 5) a better reference point to assess the effect of the therapy than baseline vision, which varies greatly depending on the disease stage at the time of enrollment in the study. Relative to the observed nadirs, average visual acuity for all LUMEVOQ-treated eyes increased beyond the +15-letter threshold (-0.3 LogMAR change) that conventionally defines clinically meaningful improvement. (See Table 1.)
Responder analyses reinforce the finding of improved outcomes for patients, for whom natural history typically results in greatly impaired vision with a very low likelihood of spontaneous recovery3. Five years after injection, patients who were bilaterally treated experienced a higher rate of clinically relevant recovery* from their nadir, compared to patients who had unilateral treatment (75% vs. 60%). 79% of bilaterally treated patients were able to read letters on a screen (on-chart vision), compared to 72% of patients treated in only one eye.
Table 1: Change in Best-Corrected Visual Acuity (BCVA) versus Nadir 5 Years after Injection
| 1st affected eye | 2nd affected eye | |
| Subjects bilaterally injected with LUMEVOQ® | LUMEVOQ®
–0.38 LogMAR |
LUMEVOQ®
-0.35 LogMAR |
| Subjects unilaterally injected with LUMEVOQ® | LUMEVOQ®
-0.40 LogMAR |
PLACEBO
-0.28 LogMAR |
Database lock: Dec 31, 2024. Subjects bilaterally treated: 1st affected eyes: n=48; 2nd affected eyes: n=48; subjects unilaterally treated: 1st affected eyes: n=50; 2nd affected eyes: n=50. p<0.0001 for all eye groups using linear mixed model.
Favorable safety profile
The favorable safety profile of LUMEVOQ® continued to be confirmed, with the safety profile of the drug being demonstrated as comparable in bilaterally and unilaterally treated subjects. There was no study discontinuation related to systemic or ocular adverse events, and there were no serious ocular adverse events. The main ocular adverse event was intraocular inflammation, which was mostly mild and responsive to conventional treatment.
REFLECT was a randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled Phase III trial involving 98 subjects with vision loss due to LHON caused by a mutated ND4 mitochondrial gene; enrolled ND4 subjects had vision loss up to one year from onset. All subjects received an intravitreal injection (IVT) of lenadogene nolparvovec in their first affected eye. The second affected eye was randomized to either a second IVT of LUMEVOQ® or a placebo IVT, which was administered on the same day or the following day. 48 subjects were randomized to LUMEVOQ® bilateral treatment, and 50 to lenadogene nolparvovec unilateral treatment (first-affected eye treated with LUMEVOQ®, second-affected eye treated with placebo). REFLECT patients were followed up to 5 years post-injection.
* “Clinically Relevant Recovery”, or CRR, refers to an improvement in Best-Corrected Visual Acuity (BCVA) that satisfies one of two conditions: (1) A 10-letter (≥0.2 LogMAR) improvement for an on-chart starting visual acuity. (2) Improvement from “off-chart” to “on-chart” (≤1.6 LogMAR).
References:
- Yu-Wai-Man P, Newman NJ, Carelli V, Moster ML, Biousse V, Sadun AA, et al. Bilateral visual improvement with unilateral gene therapy injection for Leber hereditary optic neuropathy. Sci Transl Med. (2020) 12:eaaz7423. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaz7423
- Newman NJ, Yu-Wai-Man P, Carelli V, Moster ML, Biousse V, Vignal-Clermont C, et al. Efficacy and safety of intravitreal gene therapy for Leber hereditary optic neuropathy treated within 6 months of disease onset. Ophthalmology (2021) 128:649–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2020.12.012.
- Newman NJ, Carelli V, Taiel M, Yu-Wai-Man P. Visual outcomes in Leber hereditary optic neuropathy subjects with the m.11778G>A (MTND4) mitochondrial DNA mutation. J Neuro-Ohthalmol. (2020) 40:547–57. doi: 10.1097/WNO.0000000000001045.
Contacts
-
GenSight BiologicsChief Financial OfficerJan Eryk Umiastowski
-
LifeSci AdvisorsInvestor RelationsGuillaume van Renterghem+41 (0)76 735 01 31